Strength Improvement in Pigs with CRISPR-Cas9 and Neural Network Learning
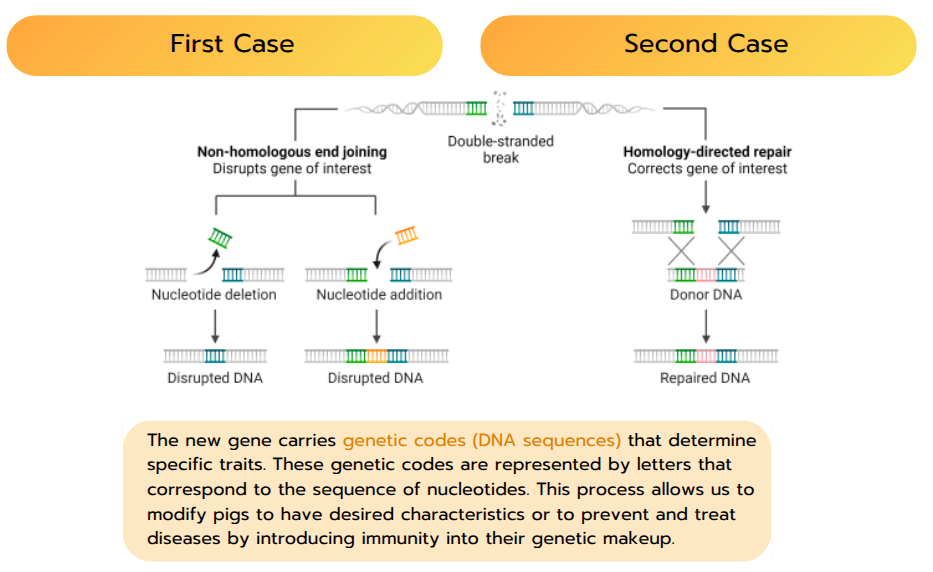
5 - 7 December 2024This project aims to reduce the time and manual effort required by scientists in genetic editing. Typically, scientists must visually inspect the positions of genes to be modified, a process that is time-consuming and prone to human error. To address this issue, the system integrates AI to accurately analyze and identify genetic locations. The main objective is to develop stronger pig breeds with improved disease resistance and to minimize the risk of zoonotic disease transmission, which has become a critical issue in the post-pandemic era following viruses such as COVID-19 that can spread from animals to humans. The use of AI technology thus enhances the efficiency, safety, and precision of genetic research. Additionally, the robot has a child-following function, utilizing AI-based detection and face recognition to ensure smooth interaction. Bounding boxes and facial landmarks are used for tracking, and when the bounding box disappears from the frame, the robot employs navigation and actionlib to follow the detected position.
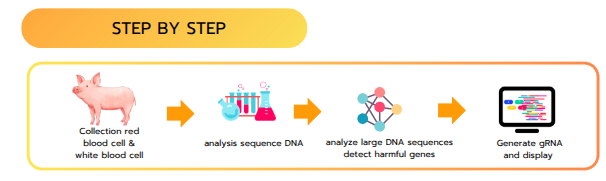
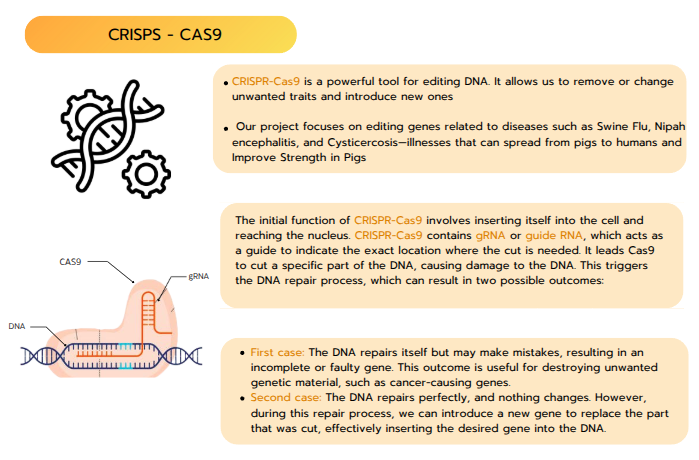
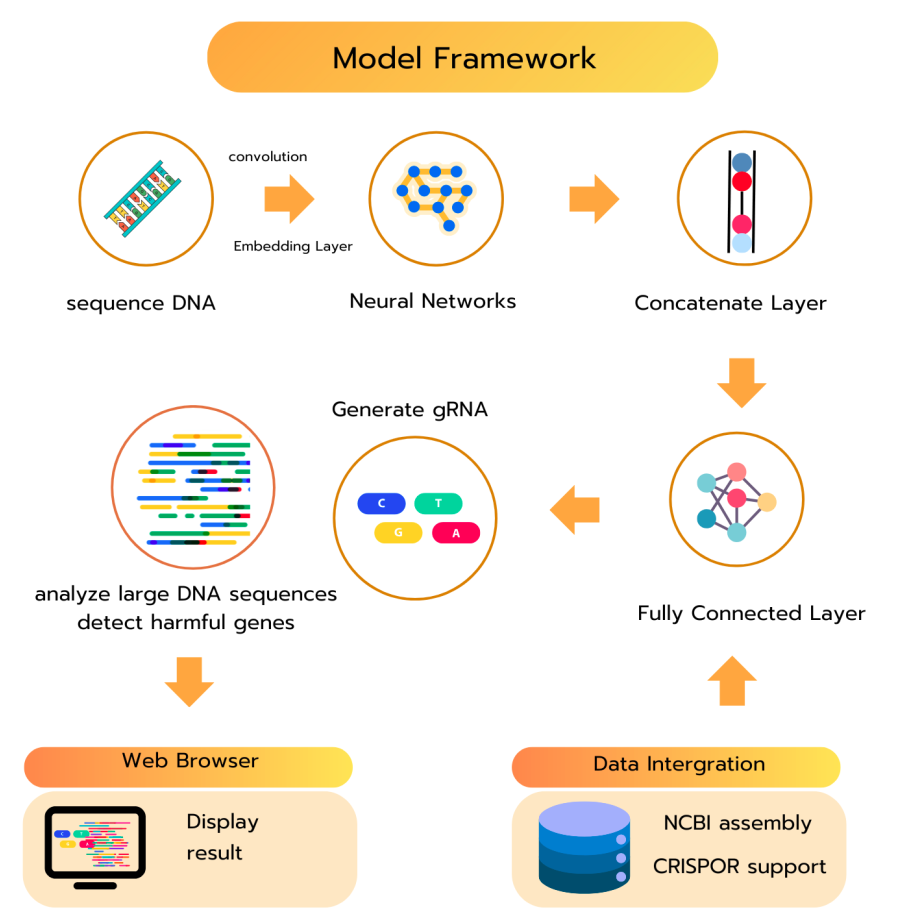
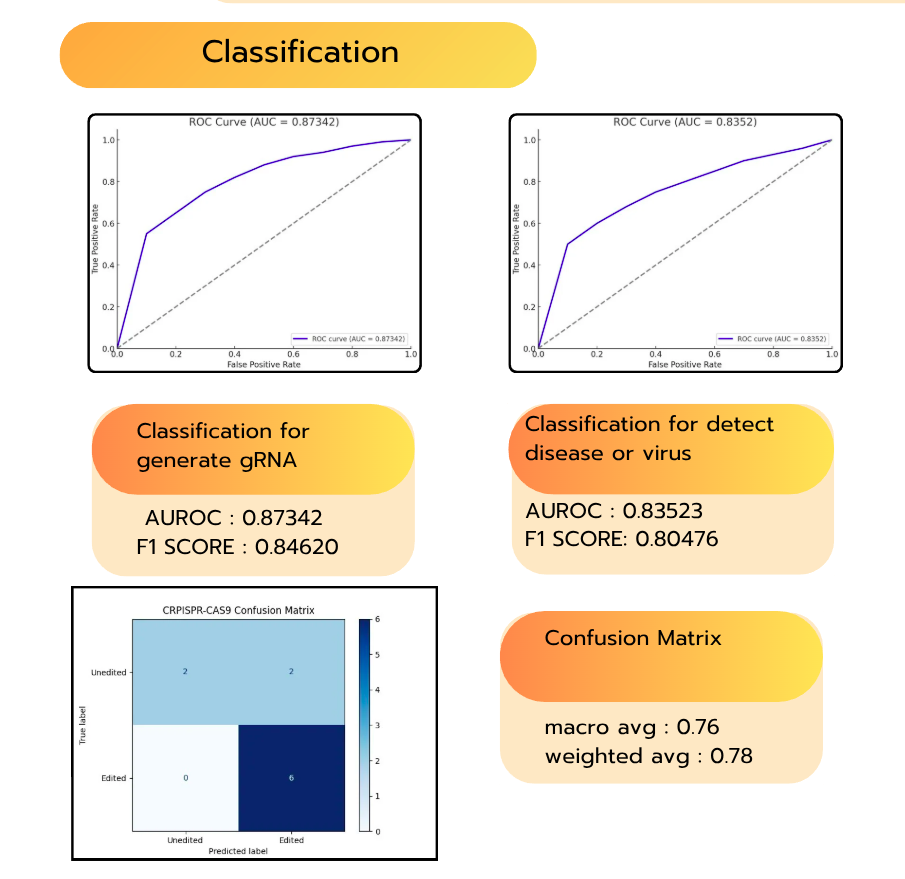
This project involved designing and developing a website as a local server system using Flask (Python). The front end was built with HTML to collect user input from scientists, while JavaScript handled data exchange between the front end and back end via the fetch API in JSON format, allowing the AI model to process and analyze the data. The AI model was developed using base-pair sequence data to diagnose disease types and identify gene-editing target sites. It then generates custom gRNAs indicating precise cut locations, and the processed results are displayed on the website for scientists to review and utilize in further research.